Static (Compile-time) Polymorphism
Polymorphism (the idea of "having many forms") is closely related to type substitution. You have already seen a flavor of it in action: you can pass an argument of type GradStudent to a method like add that takes a parameter of type Student because the compiler honors type substitution and implicitly casts from the subtype (GradStudent) to the base type (Student). This is called static or compile-time polymorphism.
Exercise Make up an example to showcase compile-time polymorphism for the following type hierarchy.
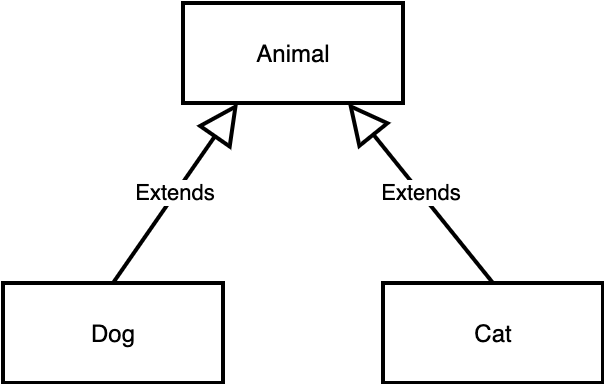
Solution
Suppose we have the following class:
public class Shelter {
private Animal[] animals;
private int numAnimals;
// Constructor not shown to save space
public add(Animal a) {
animals[numAnimals++] = a;
}
}
Objects of type Dog and Cat can be passed to the add method and be stored in the animals array.