Exception Hierarchies
The Throwable class is the super-class of all errors and exceptions in the Java language. Only objects that are instances of this class (or one of its sub-classes) are thrown by the Java Virtual Machine or can be thrown by the Java throw statement.
Exceptions are regular classes, and as such, one exception can sub-class another.
class BankingException extends Throwable {...}
class InsufficientFundsException extends BankingException {...}
class NegativeAmountException extends BankingException {...}
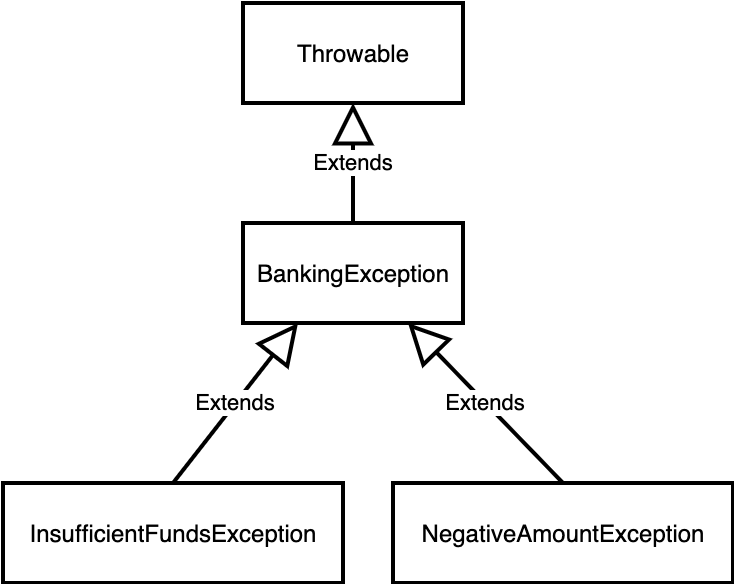
If an exception is declared to be caught, any of the sub-classes of that exception will also be caught by that same catch statement.
try {
// Some code that might throw BankingException exception
// or its sub-classes
} catch (BankingException e) {
// deal with the exception
}
When you chain catch blocks, you must deal with more specific exceptions first.
try {
// Some code that might throw BankingException exception
// or its sub-classes
} catch (InsufficientFundsException e) {
// deal with InsufficientFundsException
} catch (BankingException e) {
// deal with the exception
}