Ranked Array Representation
A complete binary tree can be uniquely represented by storing its level order traversal in an array.
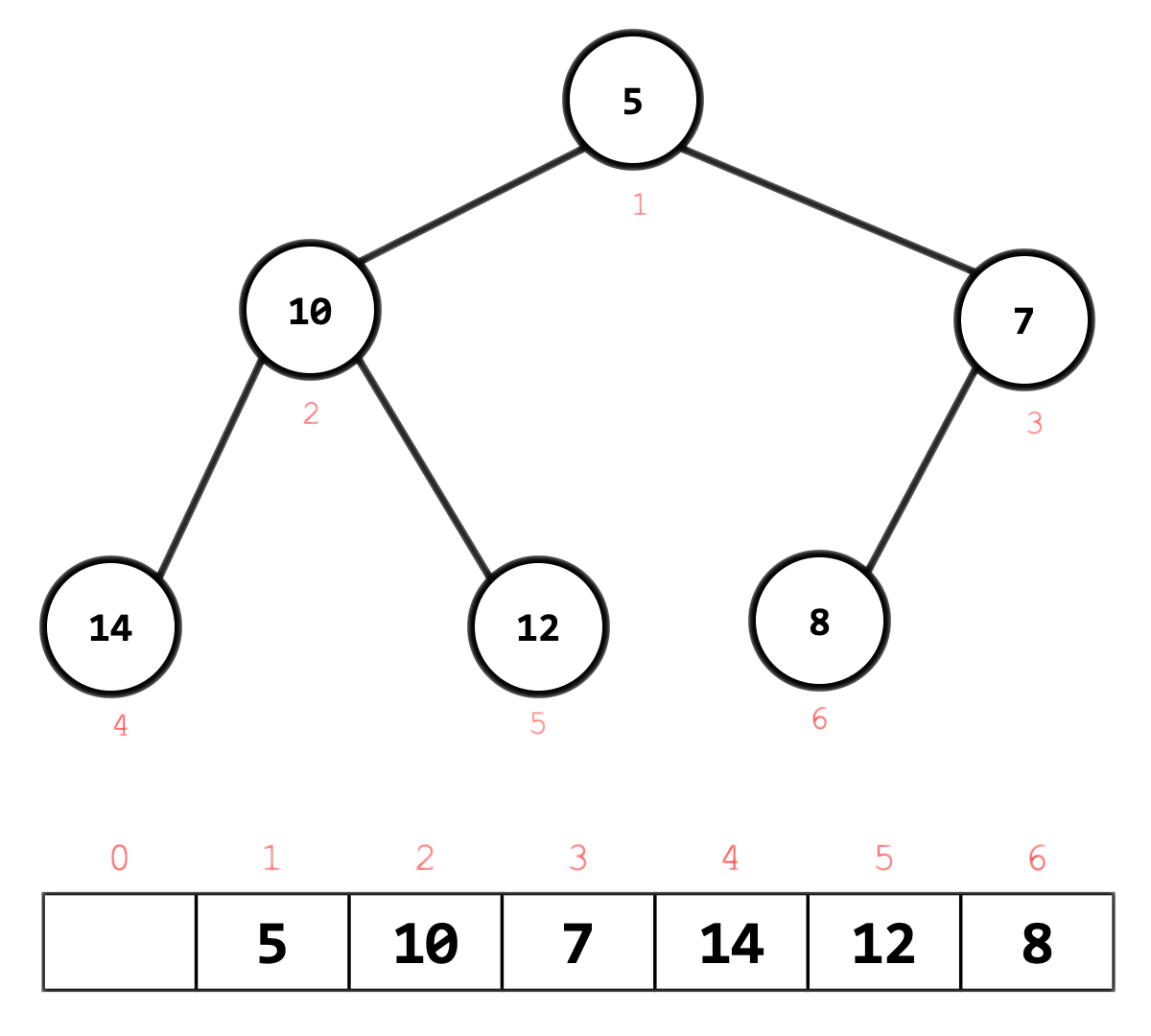
The root is the second item in the array. We skip the index zero cell of the array for the convenience of implementation. Consider $k^{\text(th)}$ element of the array,
- its left child is located at
2 * kindex - its right child is located at
2 * k + 1index - its parent is located at
k / 2index